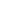PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type

What is the PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type?
PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type is a conductive adhesive developed with
innovative technology, featuring low-temperature curability. This product combines conductivity and adhesive
properties, with the ability to cure at a low temperature of 80degC.
・Low-Temperature Curability at 80degC
PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type cures quickly at a low temperature of 80degC.
It is suitable
for use with heat-sensitive electronic components and materials, significantly improving flexibility in the
manufacturing process.
・Excellent Connection Reliability
It effectively suppresses galvanic corrosion, a common issue with conventional conductive adhesives.
It
provides high connection reliability, enhancing the long-term reliability of the product.
・Multi-functionality
In addition to its conductive properties, it also features excellent
thermal conductivity and EMI shielding.
It effectively addresses both heat dissipation and electromagnetic
interference shielding for electronic devices.
These features of PLENSETTM Electrically conductive
type enable it to deliver high performance and reliability in various applications, such as bonding electronic
components, automotive parts, and assembling precision devices.
Have you experienced these issues?
Here is the product that resolves these issues. PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type
Application example
PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type demonstrates high
performance across various applications due to its excellent properties.
・Solder
Replacement
PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type cures at a low temperature of
80℃, making it a viable alternative to traditional soldering methods.
This eliminates the need for
high-temperature processes required in soldering, preventing the deterioration of heat-sensitive components
and boards.
Additionally, the need for flux cleaning post-soldering is removed, streamlining the
process.
・Die Attach Material (Heat Dissipation)
With excellent thermal conductivity
PLENSETTM Electrically conductive type can be used as a die attach material.
It enhances the
efficiency of heat dissipation from electronic components, ensuring stable operation and extended device
life. This is particularly effective for heat management in high-power semiconductors and power
devices.
・Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding
It possesses high EMI
shielding properties, making it suitable for mitigating electromagnetic interference in electronic
devices.
It helps prevent device malfunctions and reduces the impact of external electromagnetic waves,
making it ideal for seam bonding of electronic device cases and as a shielding material within enclosures.

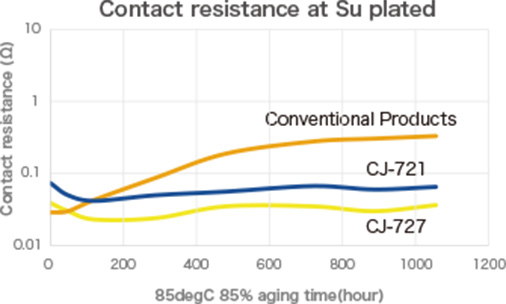
Galvanic corrosion inhibition/electrically conductive adhesives
Issues with general conductive paste
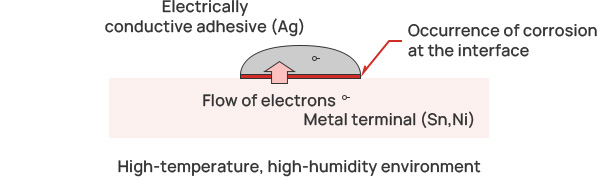
Generally, conventional conductive adhesives are composed of a dispersion of silver (Ag)
powder.
However, this composition can lead to the issue of galvanic corrosion in high temperature and high
humidity environments. Specifically, when using nickel (Ni) or tin (Sn) as terminal materials, a galvanic cell can
form due to the potential difference in such environments, leading to galvanic corrosion. This corrosion causes an
increase in contact resistance, resulting in malfunctions.
This increase in
contact resistance due to corrosion negatively affects the reliability and performance of electronic devices. In
the case of conductive adhesives (Ag) and terminal metals (such as Sn and Ni), the situation is as follows.
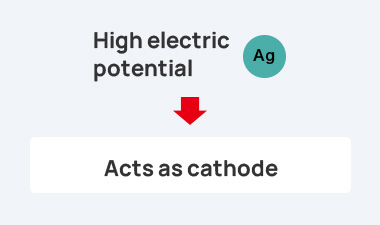
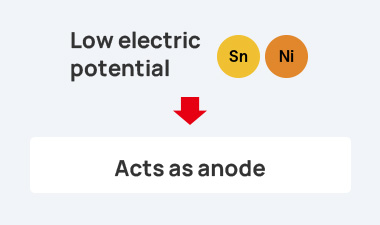
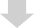
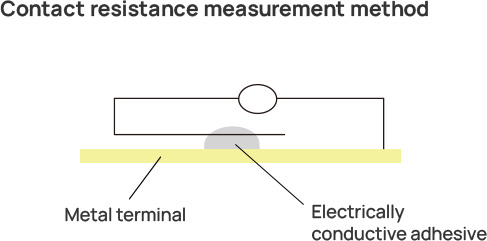
As a result, a battery is formed as shown in the figure, and the contact resistance between the electrically conductive adhesive and the metal terminal increases.
If galvanic corrosion can be inhibited...
PLENSETTM Conductive Type has the characteristic of suppressing galvanic corrosion,
which commonly occurs with conventional conductive adhesives.
This innovative feature addresses many issues and
expands the range of applications for conductive adhesives.
By using PLENSETTM Conductive Type, it
can
particularly serve as an alternative to solder. The need for reflow (high-temperature processing) and flux cleaning required with solder is
eliminated. Furthermore, the low-temperature curability PLENSETTM Conductive Type allows the use of materials with low heat resistance.
This enables the use of heat-sensitive
electronic components and materials, significantly increasing design flexibility.
These benefits greatly enhance manufacturing process efficiency and are expected to reduce
production costs.
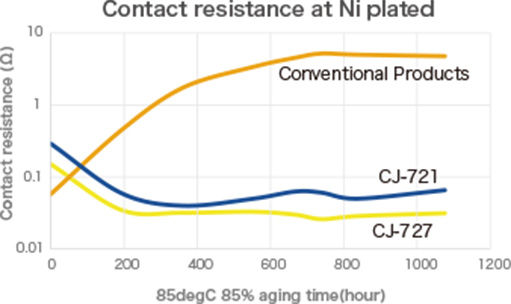
PLENSETTM Conductive Type effectively suppresses galvanic corrosion, overcoming the challenges associated with conventional conductive adhesives, and provides an excellent solution that meets diverse manufacturing needs. This innovative product enables process efficiency, cost reduction, and greater design flexibility, making it a powerful tool for maintaining a competitive edge in the electronics industry.
Electrically conductive type product details
Refer to the table below.
| Item | CJ-721 | CJ-727 | Conditions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Appearance | Silver paste | Silver paste | Visual inspection |
| Viscosity | 27Pa・s | 70Pa・s | E-type viscometer 25degC,5rpm | |
| Thixotropic index | 3.2 | 4.5 | E-type viscometer 25degC,1rpm/5rpm | |
| Standard curing conditions | 80℃×60minutes | Oven curing | ||
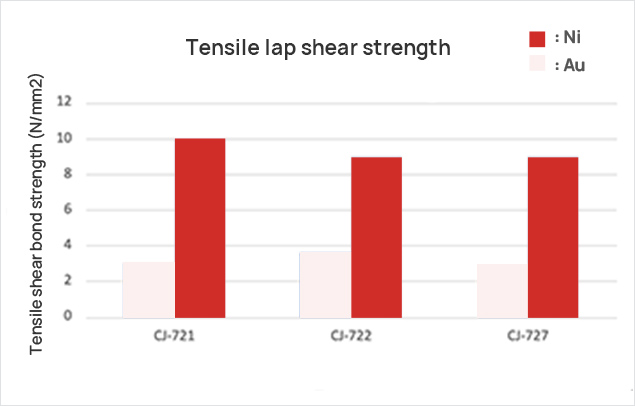
| Properties of cured materials | Tensile lap shear strength | 3.0N/㎟ | 2.8N/㎟ | Gold plating |
| 10N/㎟ | 9N/㎟ | Nickel plating | ||
| Specific resistance | 12x10¯4;Ω・cm | 5x10¯4;Ω・cm | Supporter FR-4, 25degC | |
| Thermal conductivity | 1.3W/mK | 1.8W/mK | Hot-disk method | |